SCHD, or the Schwab U.S. Dividend Equity ETF, has gained significant attention in the investment world.
As investors seek reliable income streams and long-term growth potential, dividend-focused ETFs like SCHD have become increasingly popular.
This article will explore the features, benefits, and potential drawbacks of SCHD to help you determine if it’s a suitable investment for your portfolio.
Understanding SCHD: The Schwab U.S. Dividend Equity ETF

The Schwab U.S. Dividend Equity ETF (SCHD) is a passively managed exchange-traded fund that aims to track the performance of the Dow Jones U.S. Dividend 100 Index.
This index consists of high-quality, dividend-paying U.S. stocks with a record of consistent dividend payments.
Understanding the structure and objectives of SCHD is crucial for evaluating its potential as an investment.
What is SCHD?
SCHD is an exchange-traded fund (ETF) offered by Charles Schwab & Co., Inc. It was launched in October 2011 and has since become one of the most popular dividend-focused ETFs in the market.
The fund seeks to provide investors with exposure to a diversified portfolio of dividend-paying U.S. stocks while aiming for both income and capital appreciation.
SCHD’s Investment Objective
The primary objective of SCHD is to track the total return of the Dow Jones U.S. Dividend 100 Index, before fees and expenses.
This index is designed to measure the performance of high dividend-yielding stocks in the U.S. market that have a record of consistently paying dividends and exhibit fundamental strength based on financial ratios.
Key Features Of SCHD
- Diversification: SCHD typically holds around 100 stocks, providing broad exposure to dividend-paying companies across various sectors.
- Low Expense Ratio: With an expense ratio of 0.06%, SCHD is one of the most cost-effective dividend ETFs available.
- Quarterly Dividend Payments: The fund distributes dividends to shareholders on a quarterly basis.
- Transparency: As an ETF, SCHD’s holdings are disclosed daily, allowing investors to know exactly what they own.
- Liquidity: SCHD is highly liquid, with significant daily trading volume, making it easy to buy and sell shares.
SCHD’s Portfolio Composition
SCHD’s portfolio consists of high-quality, dividend-paying U.S. stocks selected based on fundamental strength and consistent dividend payments.
The fund’s top holdings typically include well-established companies with strong financial positions and a history of increasing dividends.
The sector allocation of SCHD tends to be weighted towards industries known for their dividend-paying characteristics, such as:
- Consumer Staples
- Health Care
- Industrials
- Information Technology
- Financials
This sector diversity helps to balance the portfolio and mitigate risk while still focusing on dividend-paying stocks.
The Benefits Of Investing In SCHD

SCHD offers several advantages that make it an attractive option for many investors. From its focus on quality dividend-paying stocks to its low fees and potential for both income and growth, SCHD presents a compelling case for those seeking a balanced approach to equity investing.
Income Generation
One of the primary benefits of investing in SCHD is its potential for generating regular income. The fund’s focus on companies with a history of consistent dividend payments can provide investors with a steady stream of cash flow.
This can be particularly attractive for retirees or those seeking to supplement their income from investments.
Quality Stock Selection
SCHD’s methodology for selecting stocks goes beyond simply choosing high-yield companies. The fund looks for businesses with strong fundamental characteristics, including:
- Consistent dividend payments
- High return on equity
- Stable earnings growth
- Strong cash flows
This focus on quality can help reduce the risk of dividend cuts and provide a more stable investment over time.
Low Expense Ratio
With an expense ratio of just 0.06%, SCHD is one of the most cost-effective dividend ETFs available. This low fee structure means that more of the fund’s returns are passed on to investors, rather than being eaten up by management costs.
Potential For Capital Appreciation
While SCHD is primarily known for its dividend focus, it also offers the potential for capital appreciation. As the underlying companies in the fund grow and prosper, the value of their stocks – and consequently, the value of SCHD shares – may increase over time.
Read This Blog: How To Invest In SpaceX?
Tax Efficiency
As an ETF, SCHD can be more tax-efficient than actively managed mutual funds. The fund’s low turnover rate and the ETF structure’s ability to use in-kind redemptions can help minimize capital gains distributions, potentially reducing the tax burden for investors holding the fund in taxable accounts.
Potential Drawbacks And Risks Of SCHD
While SCHD offers many benefits, it’s important to consider its potential drawbacks and risks. The fund’s focus on U.S. stocks means limited international exposure, which could result in missed opportunities in global markets.
SCHD may also be more concentrated than broader market indexes, potentially leading to higher volatility if certain sectors underperform. Dividend-paying stocks can be sensitive to interest rate changes, which could impact SCHD’s performance when rates rise.
There’s always a risk that companies may reduce or eliminate their dividends due to financial difficulties. Lastly, like all equity investments, SCHD is subject to general market risk, with its value fluctuating based on overall market conditions and economic factors.
While SCHD offers many benefits, it’s important to consider potential drawbacks and risks associated with investing in this ETF.
Concentration Risk
Although SCHD holds around 100 stocks, it may still be more concentrated than broader market indexes. This concentration could lead to higher volatility if certain sectors or companies underperform.
Limited International Exposure
SCHD focuses exclusively on U.S. stocks, which means investors miss out on potential opportunities in international markets. This lack of global diversification could be a drawback for those seeking worldwide exposure.
Interest Rate Sensitivity
Dividend-paying stocks can be sensitive to interest rate changes. When interest rates rise, dividend stocks may become less attractive compared to fixed-income investments, potentially impacting SCHD’s performance.
Dividend Sustainability Concerns
While SCHD focuses on companies with a history of consistent dividends, there’s always a risk that companies may reduce or eliminate their dividends due to financial difficulties or changing business conditions.
Market Risk
Like all equity investments, SCHD is subject to general market risk. The value of the fund can fluctuate based on overall market conditions, economic factors, and investor sentiment.
Comparing SCHD To Other Dividend ETFs
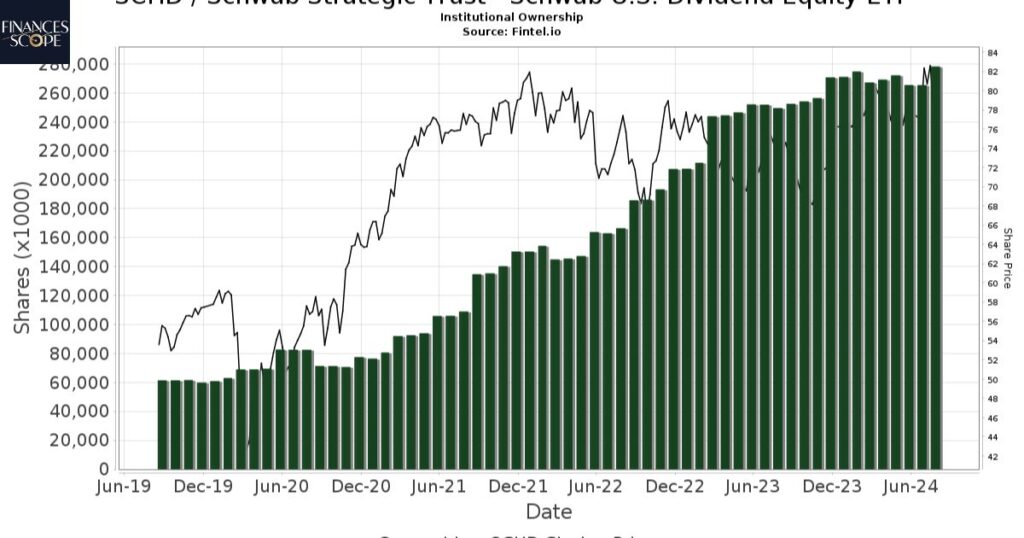
SCHD stands out among dividend ETFs due to its low expense ratio of 0.06% and focus on quality stocks with consistent dividend growth. When compared to Vanguard’s VYM, SCHD has a similar expense ratio but fewer holdings about 100 vs. 400 potentially offering more concentrated exposure.
Against iShares‘ DVY, SCHD has a significantly lower expense ratio 0.06% vs. 0.38% and emphasizes dividend growth over high current yield. Compared to SPDR’s SDY, which focuses on Dividend Aristocrats, SCHD has a lower expense ratio and considers additional quality factors beyond dividend growth streak.
While these ETFs all target dividend-paying stocks, SCHD’s balance of low costs, quality focus, and emphasis on both current income and dividend growth potential makes it a strong contender in the dividend ETF space.
To fully evaluate SCHD as an investment option, it’s helpful to compare it to other popular dividend-focused ETFs.
Read This Blog: Did Shark Tank Invest in CBD Gummies?
SCHD vs. VYM (Vanguard High Dividend Yield ETF)
Both SCHD and VYM focus on dividend-paying stocks, but they track different indexes and have slightly different approaches:
- Expense Ratio: SCHD (0.06%) vs. VYM (0.06%)
- Number of Holdings: SCHD (~100) vs. VYM (~400)
- Yield: Can vary, but historically similar
- Sector Allocation: SCHD tends to have higher technology exposure
SCHD vs. DVY (iShares Select Dividend ETF)
DVY is another popular dividend ETF, but with some key differences:
- Expense Ratio: SCHD (0.06%) vs. DVY (0.38%)
- Number of Holdings: SCHD (~100) vs. DVY (~100)
- Yield: DVY often has a slightly higher yield
- Methodology: DVY focuses more on high current yield, while SCHD emphasizes dividend growth and quality
SCHD vs. SDY (SPDR S&P Dividend ETF)
SDY focuses on the “Dividend Aristocrats” – companies that have increased dividends for at least 20 consecutive years:
- Expense Ratio: SCHD (0.06%) vs. SDY (0.35%)
- Number of Holdings: SCHD (~100) vs. SDY (~100)
- Yield: Generally similar
- Focus: SDY emphasizes dividend growth streak, while SCHD considers other quality factors
How To Invest In SCHD?

To invest in SCHD, start by choosing a reputable online brokerage that offers ETF trading. Popular options include Charles Schwab, Fidelity, and Vanguard. Open an account with your chosen brokerage, which typically involves providing personal information and deciding on the account type for example individual, joint, or IRA.
Fund your account, then use the brokerage’s trading platform to search for “SCHD”. Place an order by specifying the number of shares or dollar amount you wish to invest, and select your order type usually market or limit order.
Consider using dollar-cost averaging by investing a fixed amount regularly over time to mitigate market volatility risks. After investing, monitor your SCHD holdings as part of your overall portfolio and rebalance as needed to maintain your desired asset allocation.
For those considering an investment in SCHD, here’s a guide on how to proceed:
Choose A Brokerage
SCHD can be purchased through most online brokerages. Consider factors such as:
- Trading fees
- Account minimums
- Research tools
- User interface
Popular options include Charles Schwab, Fidelity, and Vanguard.
Open An Account
Once you’ve selected a brokerage, you’ll need to open an account. This typically involves:
- Providing personal information
- Choosing an account type e.g. individual, joint, IRA
- Funding the account
Place An Order
To buy SCHD:
- Log into your brokerage account
- Search for “SCHD” in the trading platform
- Choose the number of shares or dollar amount you want to invest
- Select the order type (usually “market” or “limit”)
- Review and submit your order
Consider Dollar-Cost Averaging
Instead of investing a lump sum, consider using dollar-cost averaging by investing a fixed amount regularly over time. This can help reduce the impact of market volatility on your investment.
Monitor And Rebalance
Regularly review your investment in SCHD as part of your overall portfolio. Rebalance as needed to maintain your desired asset allocation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the current dividend yield of SCHD?
The dividend yield of SCHD varies over time. As of [current date], the 30-day SEC yield is approximately [X]%. Check the fund’s website for the most up-to-date yield information.
How often does SCHD pay dividends?
SCHD distributes dividends to shareholders on a quarterly basis, typically in March, June, September, and December.
Is SCHD a good investment for retirees?
SCHD can be suitable for retirees seeking income and potential growth, but individual circumstances and risk tolerance should be considered.
Can I hold SCHD in an IRA?
Yes, SCHD can be held in various account types, including traditional IRAs, Roth IRAs, and 401(k) plans that allow ETF investments.
How has SCHD performed compared to the S&P 500?
SCHD’s performance relative to the S&P 500 varies over different time periods. Generally, it has provided competitive returns with lower volatility, but past performance doesn’t guarantee future results.
Conclusion
SCHD, the Schwab U.S. Dividend Equity ETF, offers investors an attractive option for gaining exposure to high-quality, dividend-paying U.S. stocks. With its focus on companies with strong fundamentals and consistent dividend payments, SCHD can provide a balance of income generation and potential capital appreciation.
The fund’s low expense ratio, diversified portfolio, and emphasis on quality make it a compelling choice for many investors, particularly those seeking income or a more defensive equity position.
However, like all investments, SCHD comes with its own set of risks and limitations, including concentration in U.S. stocks and sensitivity to interest rate changes.
When considering whether SCHD is a good investment for your portfolio, it’s essential to evaluate your personal financial goals, risk tolerance, and overall investment strategy.

Marcus Delgado is a certified financial planner with expertise in retirement strategies and tax optimization.
With a background in economics and a passion for helping individuals achieve financial freedom, Marcus provides practical advice on long-term wealth building and smart money management.












